The Standard course of action for all consumers when they enter their favorite clothing shop is- they select the best one according to their taste, check the size by placing it on their frame and then turn to check the price of the product.
Not just offline, this consumer behavior applies to online shopping too. When shopping from online store, the price of the product is right next to the product image and name. After checking the general look of a product, price is the next thing that qualifies a product for final purchase. The decision to buy or not to buy a product is taken only after this.
So, before you price a product, it is important to understand some psychological triggers that improve profits as well as customer satisfaction. Following is a list of various kinds of pricing and major triggers (associated with them) that businesses can use to their discretion, as per suitability.
1. Charm pricing
All of us have seen the charm of number 9. Every supermarket store is packed with products whose price ends with number 9. In an experiment conducted by MIT and the University of Chicago, a standard women’s clothing item was tested at the prices of $34, $39, and $42. The item that was sold the most was priced $39, even more than the cheaper $34 price.
2. Round Number pricing
According to strategy business, 57% customers prefer whole dollar amounts (e.g. $10) and 4% are okay with half dollar pricing (E.g. $10.50) Some people prefer simple pricing rather than messy pricing as the latter just distracts and seems unnecessary. The image below depicts why different type of people get attracted to different pricing. If you own a business or are about to launch, you need to understand this about your target audience before pricing your product.

3. Syllable
The number of syllables or how we read/pronounce a price affects the decision-making process of online buyer. The one which is easier to pronounce converts better than longer syllable pricing. For instance, among twenty-seven eighty five and twenty-seven sixteen, the latter will convert better as it is easier to pronounce.
4. Anchor effect
Placing premium product (or service) along with standard ones increases sales of the standard option. Customers view the less expensive option as a good bargain (compared to the higher cost product). Selling a $2000 watch is easier when you put it next to a $10,000 watch.
Also Read: 6 Creative Ways to Promote Your Product on Social Media
5. Omit the currency sign or use small fonts
According to Cornell researchers, customers see a currency sign as a metaphor for the pain of spending. Currency sign like $ creates an unconscious cognitive barrier to spending. When the currency sign is present, customer concentrates on the price rather than the product. To increase the chances of conversion, businesses should omit the currency sign completely or keep the font of the sign smaller than usual.

6. Think of 3c’s
When you are about to decide the price of your product, put it through the lens of Cost, Customer, and Competitors. Do not let just one factor dictate your pricing strategy. The amount of money you spend to create the product/service, the categories of customer you are trying to sell your product and the price range of your competitors, all must be taken into account. Considering these things, you will be able to come up with the perfect pricing.
7. Odd Numbers
According to a study by Marketing Bulletin in 1997, a consumer prefers to buy products whose price end with odd number especially 5, 7 and 9. If a product is priced $47, customers would readily buy it instead of buying a $46 product.
8. Useless price points
Dan Ariely explains in his theory that a business should try and add a useless option along with their products. While no one will choose the useless option, it may make the other product with similar pricing more attractive, thus increase sales. Understand more about such useless options below.
The Economist reportedly offered three different subscription offers
• A one-year online subscription – $59
• A one-year print subscription- $125 (Useless option)
• One year online and print subscription – $125
Dan Ariely conducted this experiment and found that among all pricing options, 84% of people chose the third option. In the second experiment, he removed the useless option and checked the results. Surprisingly, 68% people chose the first option and 32% chose the third.

9. Buy one get one free
This pricing strategy makes the customer pay the full price of one product/service to get another free. The psychology that is working is greed. When customers come across an offer, they forget their logics and buy the product just to get the free item. Besides giving a free item, you can tweak the offer in different ways, like-
-Buy one and get 30% discount on second product
-Buy 3 get one free.
All these options will have the same effect as BOGOF (buy one get one free).
10. Scarcity
This psychological trigger if used wisely works wonders with people. The less the quantity of product/service, the more is the perceivable value. Expedia uses this technique on their pricing page.
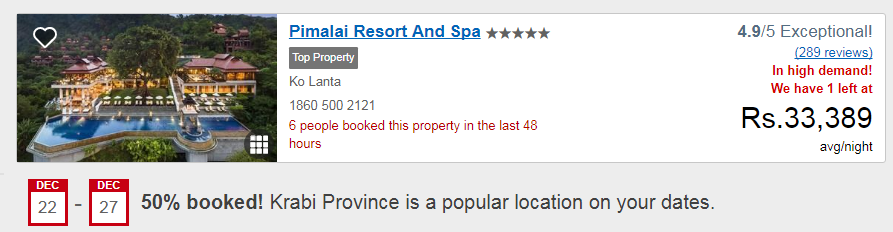
This way they entice the customers, that the hotel is in high demand and the customers should book before losing their chance.
11. Customer-segment pricing
In some cases, different customers can be charged differently for the same product/service. For example – The entry charges for a theatre for a student or senior citizen is much less than normal entry charges.
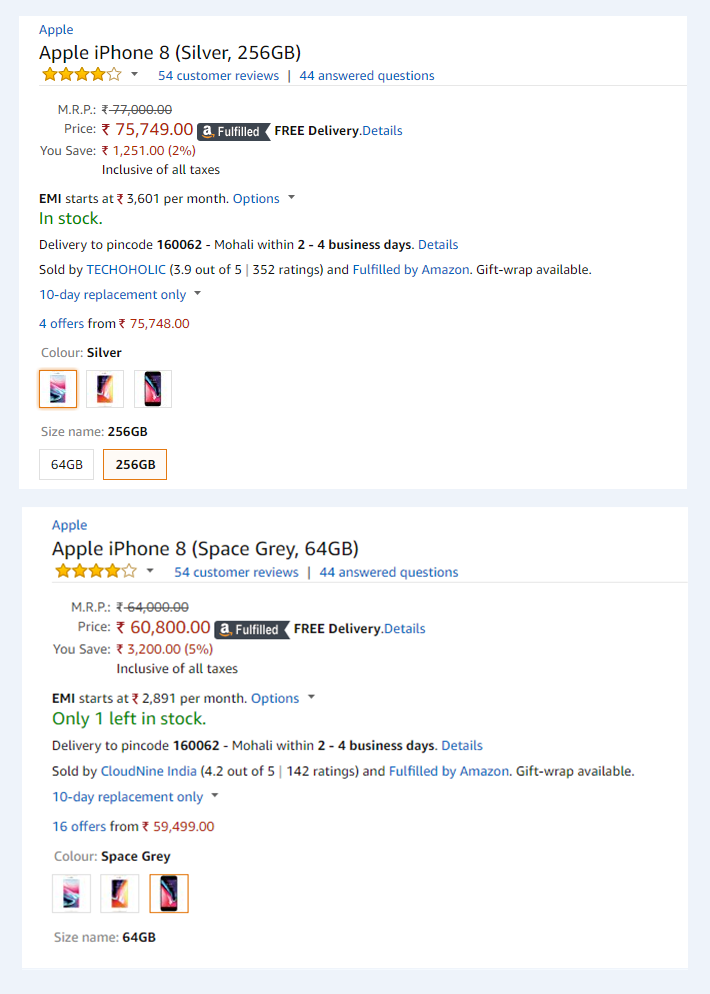
12. Product-form pricing
Different version of the same product is priced differently but it is not always proportionate to their cost. The difference of price between iPhone 7 – 32 GB and iPhone 7 – 256 GB is an apt example of this sort of pricing.
13. Prestige pricing
Prestige pricing is also Known as image pricing, this is one of the most widely used practices. Some companies price their products artificially high, just for the sake of image that it brings along. Products are priced high only for the exclusivity or luxury that they bring to a customer. Luxury goods are specially priced this way.
Also Read: Buyer Behavior Insights and Data Sources to Increase Ecommerce Sales
14. Channel pricing
The place from where a product/service is bought is a big factor considered while pricing a product. The price of a product/service is different when bought from different channel in the same city. For example:- When a bottle of water is bought from a five star restaurant from ABC city it is priced differently as compared to water from a local vendor.
15. Location pricing
The same product is priced differently in different locations, even though the cost of the product is similar but the retail price differs at different places. Government policies, transportation cost and other such factors play vital role in determining such prices. For example: – the price of Lays chips when bought normally and when bought from a tourist destination differ considerably.
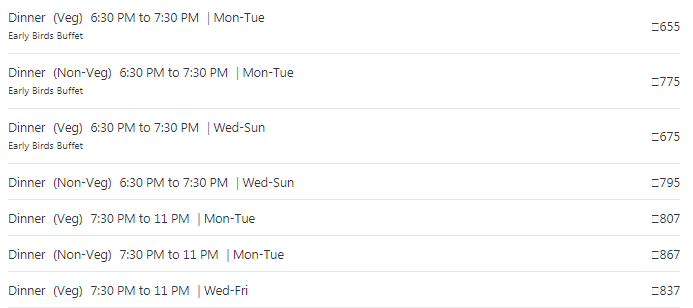
16. Time pricing
Prices of a product vary according to time/day/season, etc. The best example to explain this is restaurants change their prices of weekdays and weekends on a regular basis. You must have seen that early bird dinner prices are different from normal dinner prices; that’s also a form of time pricing.
Also Read: How to Ensure That Your Product or Service Will Be Adopted by Masses
17. Psychological discounting
Psychological discounting is when a product/service is priced higher and then a discount is offered on it. This strategy is usually adopted by e-commerce platforms during sales as it is a zero-loss game.
18. 10 for $10
We have all seen this offer in supermarkets. Consumers think that they have to buy 10 products to avail the deal, so they will load their shopping cart. This offer plays with the psychology of the consumer and leads to increasing the sales of the product.
19. Time over money
Researchers suggest that entrepreneurs should quit selling the product for money and start selling it for time. If the brand wants to offer personal experience to their customers, they must focus on making their time memorable.
For instance, the two distinct signboards at a lemonade stall read,
1) Spend a little time and enjoy ABC Lemonade
2) Spend a little money and enjoy ABC Lemonade
The sign stressing time attracted twice as many people to buy lemonade who were willing to pay twice the amount.
20. Longer payments terms
Now that everything is available on easy EMI option, companies have stretched the payment over a longer period. Longer payment terms allow sellers to lower the monthly payment amount. Consumers often worry less about the interest rate rather they check whether they can afford the monthly payment or not.
21. Power of context
Economist Richard Thaler researched regarding the power of context. Consumers are ready to pay higher prices of a particular product if they are given subtle cues that justify the premium prices. Perception plays crucial role in influencing their evaluation of prices.
For example – People prefer “multimedia course” over an eBook, even if the information offered is exactly the same.
22. Some people believe more the price, better the quality
For few products, consumer believes that higher the price means higher the quality. This is especially valid for beauty products. So while pricing a product keep in mind the quality/category of the product.
Also Read: Product Selling & Customer Experience Rules are Similar Online and Offline
23. Discount pricing
It is no secret that consumers love sales and discounts. From increasing traffic to offloading unsold inventory, there are several reasons why sellers offer discounts. Adding discounts to your pricing will help in attracting price-sensitive customers to your website.
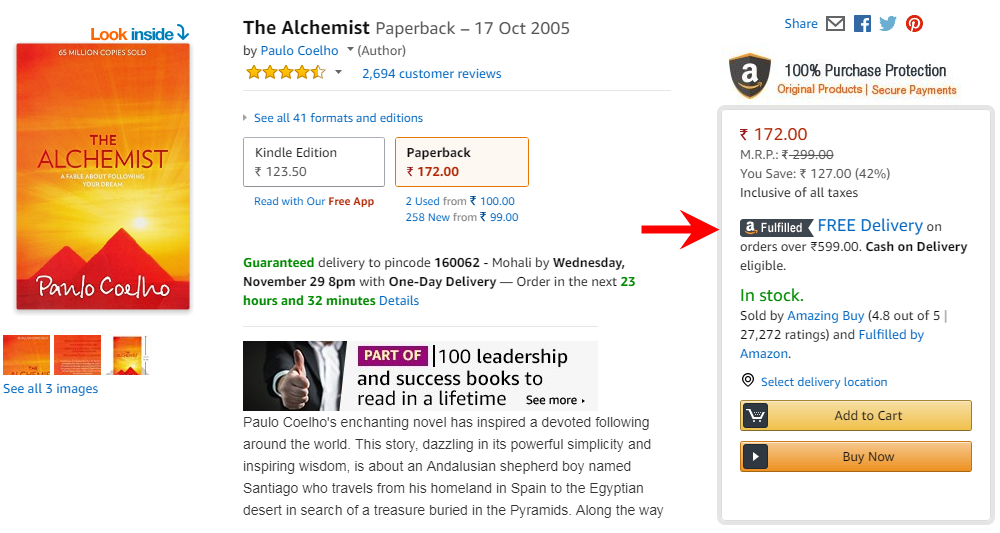
24. Free shipping/ warranty
When the word free is allied with the price of the product, the consumer is attracted towards it inevitably. Marketers often combine free shipping/warranty with an expensive product to persuade consumers to buy it.
How should websites place the pricing on product page for maximum conversions?
25. Keep the font smaller
Researchers at Clark University and the University of Connecticut found that consumers perceive the price to be lower if the font of the price is reduced. The theory is that the human mind connects physical magnitude to numerical magnitude.
26. Comparing price (not always best)
Most entrepreneurs use this strategy to compare prices of product/services. It is a very good practice to show customers the different price range of the same product. However in some cases, it may hamper your sales strategy.
For example – A price comparison between the different seller of an e-commerce website is good while if there is price comparison of a specific medicine, customers would want to buy the expensive option rather than the cheaper as they are looking for quality over pricing.
27. Highlight discounts
When you offer sale prices along with previous price side by side- you make more sale as customers see the difference in the amount and calculate the money they are saving. To make this price strategy work, many sellers use the trick of changing the font, size, and color of the discount price.
Also Read: Colors & Conversions of a Website have a Deep Connection
28. Define what are you appealing- utility or pleasure
It is very important that the entrepreneur knows the target audience. Check whether the audience of the website is conservative or liberal spenders. An effective way to target the conservative is by focusing on utility and an effective way to pitch it to the liberals is by focusing on pleasure.
29. Reframe product value
When a product is available with EMI option, the seller needs to be very careful how they write the price of the product. Consumers like to evaluate the monthly cost to them rather than yearly. It is better to write $84/month rather than $1,000/year even though the average is same.
30. Make the context smaller
In a study by CMU, it was found that when the context of the price is small, it extremely affects the consumer psychology. You must have seen (or experienced) yourself that “$5 only” seems more tempting than $5 when you are going through a store. Here, the word “only” brings out the context of “smallness” and makes up buyer’s decision to spend those “$5”.
Final thoughts
Pricing a product is the trickiest part when you are ready to start your ecommerce business. While pricing a product, you require experimental attitude coupled with the intuitive feel for how you want your brand/product to be perceived in the market.
If you price the product too low, you will be able to get a lot of sales but your revenue might take a dip at the end of the month.
If you price the product on the higher side, you will give out a sense of luxury thereby attracting better-off clients. However, if the consumer finds a competitor with the same quality of product at lower price, they would surely shift.
That said there is never a wrong or right approach of pricing a product; it is all about understanding the value of a product and target audience. Experiment with the pricing and check which of the above-mentioned psychological trigger works for your business.









