Last Updated: June 16, 2023
Historically, the transformation driven by Web 2.0 laid the foundation for the flourishing of the eCommerce industry, propelling retail giants such as Amazon, Alibaba, and others to revolutionize the retail landscape.
However, over time, challenges arising from the centralization of power have surfaced, resulting in the increasing dominance of more prominent players in the space. This challenge has made it difficult for new entrants to compete fairly with established industry leaders.
As technology continues to advance and evolve, it offers alternative approaches to achieve desired objectives, enhancing current processes and offering solutions to challenges within them.
Web 3.0 is that cumulative shift in the web that contemporary technologies promise to bring. It is the potential solution to challenges within eCommerce. The Ethereum blockchain-driven underpinnings in Web 3.0 propose to create an open web for all users – and in the process level the playing field in the eCommerce industry, providing equal opportunity to startups to compete with more prominent players in the ecosystem – catalyzing the next big transformation.
In this blog let’s first understand what Web 3.0 is, and which technologies are driving the change. Based on that, read how Web 3.0 eCommerce technologies can bring about the necessitated shift in the eCommerce ecosystem – opening up fascinating opportunities for startups, and existing businesses, while also promising better shopping experiences for consumers.
Table of Contents
Web 1.0 to Web 3.0 – The Evolution
Change is a gradual process, individual microcosms within an ecosystem keep changing and evolving. But these changes, at times, mature to collectively bring about seismic shifts, fueling major shifts in the entire ecosystem.
For instance, human history is segregated into phases of Ancient, Medieval, and modern eras. While humans have gradually kept on progressing and evolving, this segregation is based on significant moments in the continuous development of mankind – for example, the Renaissance that propelled human civilization towards greater progress – marks the transition from the medieval period to the modern era.
Likewise, the segregation of the web into 3 phases (and beyond) signifies crucial technological development that has led and will lead to enhanced capabilities in the entire ecosystem – resulting in transformative user experiences and enhanced business opportunities.
Let’s track the development phases and understand the transition from web 1.0 to web 3.0.
Web 1.0 – The Start
It was the earliest version of the web – wherein publishers developed static web pages with limited interactive elements. The content was primarily text-based and uni-directional. The end-users could only “read” what was already published. In fact, it is referred to as the read-only web.
Documents could only be sent over the internet. The static web pages did support images and gif files.
Also, HTML 3.2 elements were evident in the form of tables, frames, and others. The forms were sent via email. The content was saved over the server’s filesystem, and not over a DBMS (database management system).
Web 2.0 – Greater Possibilities
This version of the web is currently in use. At least, the majority of the web over the internet falls under Web 2.0. Here, the number of publishers has grown exponentially. User interactivity is encouraged. UGS or user-generated content is part of the content on offer.
Interactivity has been further enhanced by the range of content or media that can be shared or consumed over the internet.
In fact, websites like Facebook and Youtube are built around UGS. Moreover, eCommerce websites like eBay allow users to transact, and information storehouses like Wikipedia have facilitated information transfer.
Web 3.0 – The Shift
The third major paradigm shift in the web is being driven by blockchain and other key technologies. (explained in the following section). It promises to truly personalize the web experience for the users. Added context to user personas, made possible with blockchains, will lead to personalized browsing experiences, with higher security.
The same benefit will be extended to web publishers, businesses, eCommerce websites, and others. They will have more effective tools to reach the target audiences.
Let’s delve into this a little further to understand how Web 3.0 eCommerce will transform experiences.
Key Technologies Driving Web 3.0 Change
“Over the next 2 to 5 years, the convergence of 5G, artificial intelligence, augmented reality and virtual reality, and a trillion-sensor economy will enable us to both map our physical world into virtual space and superimpose a digital data layer onto our physical environments.” Peter Diamandis – entrepreneur, visionary, physicist, and the CEO of Zero Gravity.
The script of science fiction a few years ago, our reality is transforming with lines between the physical and virtual worlds blurring. Let’s first take a look into the technologies driving this change
Impact of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
At the core of web 3.0 transformation is distributor ledger technology. For eg. blockchain.
A blockchain is a data ledger that is unchangeable. The ledger can store data related to transactions and other such information. Once the data is stored it cannot be changed. The blockchain then can be shared across systems. Significantly, blockchains are not centralized. They are exclusive to the systems that share them.
Thus, Web apps developed with blockchain technology will be governed, maintained, and even added onto by nodes. The data of these apps are distributed in multiple locations simultaneously, without a single controlling authority, making the apps inherently decentralized.
Additionally, according to IBM, distributed ledger technology is inherently secure and not prone to hacking.
At the moment blockchains are used to record transactions, and they are further associated with tangible or digital assets.
The technology will further allow peer-to-peer information exchange. These can be end-users, corporations, or machines.
Critically, there will be no need for middlemen that manage and own the information. And this solves the current problem of centralization.
With Web 2.0, the biggest pain point has been the ownership of user data by companies such as Facebook, Amazon, and others.
Leveraging blockchain technology, Web 3.0 can potentially disrupt the current digital landscape with decentralization resulting in far-reaching implications, and will lead the way for a more open-connected web.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Both these technologies enhance the computational capabilities to understand and evaluate unstructured data. Furthermore, AI can self-program, continuously add to its information base, and implement decisions based on the context of the situation.
The objective ― or the direction of the evolution of AI and ML is to make the web semantic, as visualized by Tim Berners-Lee (An English computer scientist and founder of web 2.0). In other words, to foster a scenario wherein users and machines will work together – cohesively.
Faster Network
More capabilities also mean higher data transfer. With data moving to the cloud for faster and more secure computing needs, the data transfer needs to facilitate the data transfer requirements.
Faster connectivity from technologies such as 5G, continuous progression of WiFi technology, and other developments in this regard holds promise to fuel the necessitated support.
Augmented Reality (AR) and IoT
AR and IoT wearables have been changing the way users interact with content. With the continued progression of their technologies, the following outcomes will have a significant bearing on Web 3.0. They promise the following outcomes contributing to the Web 3.0 promise.
Increased Interactivity
Web 1.0 solely relied on desktop monitors. Web 2.0 added mobile screens to the mix. Web 3.0 will see an increased role of AR devices, wearables, and IoT.
Consumers will be able to interact with the content more intuitively. From just clicking on desktops to touch-sensitive devices to the interconnectivity of IoT, Web 3.0 opens up opportunities for users to interact with AR devices such as AR glasses, IoT wearables, and more.
More Input Data Collection Sources
Data input points are continuing to grow as well. In addition to text inputs: gestures, voice, and others have added to the ways users interact with machines. For instance, users have also started to use IoT wearables like smartwatches that constantly monitor biometric data. That is an additional stream of data that users are providing via these devices.
Similarly, IoT devices such as household appliances, monitors tracking infants, smartwatches tracking health biometrics, and other appliances with sensors generating input data ― are increasing.
In the B2B space, the scope of IoT devices is increasing even further. IoT devices with sensors are being increasingly adopted in manufacturing, automotive, healthcare, and other sectors.
According to Statista, there were about 9.7 billion Internet of Things (IoT) devices worldwide in 2020. This number is forecasted to almost triple to 29 billion IoT devices by 2030.
Henceforth, the devices generating input data for the web is stated to increase significantly in Web 3.0.
Key Features of Web 3.0
Summing up the impact of the evolution of technologies ― the following key features of web 3.0 can be anticipated:
Decentralization
With an increased amount of user data generated, digital trust will be a key component that promises to encourage participation in the web, both for users and businesses. Decentralization is a critical component of web 3.0.
Omnipresent
An increased number of devices connected to the net means that the web is moving beyond desktops, and mobiles and transcending onto devices that are in use ― home appliances, automobiles, healthcare equipment, and others.
Semantic
As Tim Berners-Lee envisions it “The Semantic Web is not a separate Web but an extension of the current one, in which information is given well-defined meaning, better-enabling computers and people to work in cooperation.”
In other words, enhanced capabilities of the machines to better understand the data, and process it in a way humans do, leveraging the evolving technologies of AI/Ml ― will be the hallmark of Web 3.0.
Boundless
The popular game “Pokemon Go” gave the world a glimpse of how the digital space is evading boundaries and transcending the physical world. Web 3.0 entails greater possibilities with the blurring of boundaries in the physical and virtual world.
Web 3.0 and eCommerce

In the past decade, eCommerce has exploded onto the scene, especially in the post-pandemic scenario.
But, in the broader perspective, this was just the start. With the continued progression of technologies on all fronts or web 3.0 as we are calling it, eCommerce can potentially witness transformative, multi-faceted changes.
Web 3.0 eCommerce (R)evolution – From the Consumer’s Perspective
In the Web 3.0 context, the implications on consumers can be discussed first, because the third phase in internet evolution puts the spotlight on the users. They will start experiencing the web in the following new ways:
Data Ownership
At the moment, bigger eCommerce players like Amazon use a “Collaborative Filtering Engine”. A CFE analyzes consumers’ shopping behavior to predict their future purchases. Accordingly, product recommendations show up on the web pages based on consumers’ own shopping preferences and that of others.
Effectively, this may imply that leveraging mined data coerces impulse shopping. Investopedia believes these suggestions lead to a third of Amazon’s total sales.
Moreover, companies like Amazon have leveraged customer data into refining their business, to a point of introducing their own product range based on this data. While consumers have appreciated these benefits, this has also meant that these companies have gained an unchallenged competitive advantage ― cannibalizing smaller players.
Consumer sentiments toward ownership of data are changing, especially in the post-Snowden era.
A survey posted in NYTimes back in 2015 revealed that 55 percent of the survey respondents disagreed that “it’s O.K. if a store where I shop uses the information it has about me to create a picture of me that improves the services they provide for me.” And 91 percent of respondents disagreed that it was fair for companies to collect information about them without their knowledge in exchange for a discount.
Web 3.0 is set to change that scenario with DLT technology wherein the users will own their data, stored in the blockchain.
Decentralization promises to give consumers ownership of their data including monetization options driving the monopoly away from the big corporations, currently in charge.
The way this is expected to work is:
Consumer data blockchains will be owned by the consumers themselves. These assets will be portable. Similar to luggage in the physical world. Travelers can choose a lodging of their preference, they simply take their luggage to the selected place of stay. Similarly, consumers can choose to use these assets with the eCommerce platform they want to shop on. Once they want to move on to another platform they will be able to move onto that platform along with the assets they own. They plug their assets out of the old platform and plug those assets into the new platform.
Theoretically, they will also be offered monetization opportunities for these assets.
A current example of something similar taking place is the offer by NFT marketplace LooksRare to new users, who are willing to move from OpenSea to their platform.
So effectively, Web 3.0 aims to build an open web, giving the consumers the prerogative, onus, and ownership of their data.
Hyper-Personalization
Web 2.0’s cookie and consumer data-driven personalization lead to tailored suggestions. But they are based on browsing, shopping behavior, and other estimates about the consumer. Moreover, they also put into perspective what online retailers prioritized selling.
As discussed above, with Web 3 eCommerce businesses will have consumer-owned blockchain data about their personas and preferences. The data will provide better insights into the companies.
Additionally, the advanced data-crunching capabilities of AI and ML will lead to better validation of the data.
The result will be a hyper-personalized shopping experience for the consumers that truly puts them into perspective. It will put into context the consumer’s intent behind making the product search and add their preferences into perspective as well to deliver hyper-personalized search results.
Moreover, with the progression of AI and ML ― the evolution of voice assistants like Siri or Alexa into bots that “understand” the user and function as personal assistant bots are on the cards as well.
With these advancements, consumers in Web 3.0 will be able to shop from any eCommerce platform and buy products that fit their needs the best.
For instance, consumers searching for a dress to buy online, will get results based on their preferred size, color, brand, and more. The consumer will further be able to view customer reviews relevant to their preferences.
This benefit will also be extended in the B2B space as well. For instance, a manufacturing plant uses the chemical XYZ in the manufacturing process. The tank with the chemical will have sensors. Whenever the chemical dips below a specified level, automated bots will be able to bid for more stock of the chemical with the right specifications on B2B eCommerce websites and place the order for the same as well.
Intuitive Shopping Experiences
With the extension of the benefits mentioned above, and leveraging the evolving capabilities of AR as well – the buying experience of consumers in web 3.0 eCommerce is set to evolve to open up new opportunities.
AR is at the interactive end of eCommerce, or the front-end. It can blend the virtual world with the real world.
The applications are endless – consumers will be able to buy products by virtually visualizing their look and feel. Products for home decoration, furniture, and others can be analyzed for their size and fitment in the real world.
Ikea Place, Ikea’s AR app is already leveraging the technology to enhance the shopping experience of their customers.
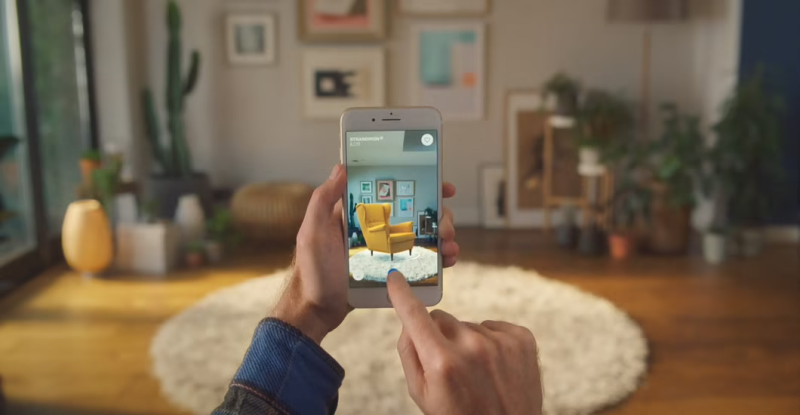 Source: IKEA
Source: IKEA
In the B2B space as well, AR can help businesses analyze the products better. B2B purchase decisions are data-driven and AR feedback would help procurement teams to analyze the product before committing to the high volume orders.
Overall AR promises to enhance the shopping experience by fostering informed and engaging purchase decisions. Furthermore, the technology reduces return rates for the products.
P2P Interactions
Without a centralized ecosystem, and with the availability of DeFi (Decentralized Finance), consumers can experience P2P eCommerce with a fresh perspective and enhanced capabilities.
The P2P business model will get a boost in the open Web 3.0.
Web 3.0 Evolution in eCommerce from the Businesses’ Perspective
Web 3.0-driven open web ecosystem is set to disrupt eCommerce as we witness it currently. It changes how businesses will approach online retail.
Along with the benefits that extend to consumers, which effectively enhances eCommerce growth, Web 3.0 is likely to extend the following benefits for businesses:
Bigger Opportunities
Web 3.0 is being viewed as a major disrupter in the eCommerce industry for startups and smaller online businesses.
As discussed, in the current scenario, the customer-content driven shopping experience and the trust of security make consumers more likely to shop from the more prominent players in the eCommerce space such as Amazon.
According to Inviqa, 59% of consumers start their online shopping journey from Amazon.
Web 3.0 is expected to level the playing field with DLT-backed consumer-owned data. Moreover, with the shift in onus of data security to the DLT technology, businesses can see eCommerce Web 3.0 being more secure, which will help such businesses in negating the advantage of the more prominent players.
Significantly, eCommerce businesses with well-defined USPs will stand a better chance at winning consumer attention.
Advertising and Marketing
Webpage advertising strategies hold immense value in web 3.0. eCommerce websites will gain enhanced capabilities by leveraging user data coupled with greater computational capabilities of AI and ML to flash consumer-centric and highly relevant advertisements.
Additionally, the marketing strategies of eCommerce businesses will be in a better position to target the customer with contextual marketing content.
Niche Industries Opportunities
With the evolution and increased penetration of interactive technologies such as AR, multiple eCommerce opportunities open up.
B2B, fashion, real estate, travel & tourism, event management marketplaces, and many other niches stand to benefit from wider adoption of AR.
Evolving eCommerce Ecosystem
Beyond websites, eCommerce is equally reliant on supply chains, digital economy, and other supportive factors of the ecosystem that orchestrate online retail.
While we have discussed the impact of Web 3.0 on eCommerce websites in this section.
Web 3.0 technologies will impact eCommerce operations as well by streamlining them.
For instance, companies like Modum leverage blockchain to digitize supply chains and provide transparent and traceable logistics of sensitive goods. They enabled Swiss Post, the national post service of Switzerland, to offer temperature-controlled, last-mile delivery.
Once these technologies gain traction, the benefits will be extended to the eCommerce industry in the long run.
Challenges for Web 3.0 Implementation at Present
Web 3.0 holds immense potential for eCommerce and in bringing about the evolution of web-driven experiences and business models. But like any new technology, there are a few challenges that will need to be addressed before it is extensively adopted.
Accessibility
Retrospectively, eCommerce gained traction with the availability of multiple devices like mobile phones, tablets, and others alongside desktop computers. These devices offered portability and convenience and made eCommerce more accessible ― augmenting its popularity. Furthermore, the industry gained traction in significant markets such as South East Asia, post the availability of low-cost mobile phones in these regions.
Accessibility is one of the major contributors to the popularization of technology.
Web 3.0 will have to cross this hurdle and be accessible and convenient to the masses in the way that web 2.0 has been over the past few years.
The current devices do not have the requisite infrastructure in the form of necessary sensors, browsers that support the technologies, and others.
Until the time the technology is not made available to the masses on low-cost readily available hardware, the popularity of eCommerce web 3.0 will be slow progress.
Costs of Implementation for Startups
Given the current scenario of the aforementioned technologies, development costs are higher. Higher development and maintenance costs impact the long-term viability of the project.
In contrast, web 2.0-driven eCommerce websites can be conveniently set up with quality turnkey solutions with minimized time to market and are less resource-intensive.
There is still time when Web 3.0 can reach this level of maturity.
Get Started Now with Market-ready Contemporary eCommerce Marketplace Solutions
Speed and Scalability
Due to the involvement of multiple nodes in the process, progress can be slow. Especially, in the case of transactions. eCommerce transactions can scale voluminously. The current status of DLT technology requires further development to offer performance with scalability.
Validation of Consumer Data
Although AI is being developed to evaluate unstructured data, it will have to evolve even further to be able to validate unscrupulous and misleading data.
Regulations Control & Ethics
According to Jack Dorsey, Founder of Twitter “You don’t own web3. The VCs and their LPs (limited partners) do. It will never escape their incentives. It’s ultimately a centralized entity with a different label. Know what you’re getting into.”
While, on an interview at TechCrunch, Bill Gates, co-founder of Microsoft says about NFTs and cryptocurrency “100% based on greater fool theory,”
It is still unclear how a decentralized network will be regulated.
Moreover, extensive use of technologies such as AR and VR also poses ethical questions. For instance, how will these impact users in the long term? With technologies that blur the line between the physical and the virtual world, will the users stop relating to the former?
While the challenges pose valid questions regarding the extensive implementation of Web 3.0, the answers to these will be more clear with time.
To Sum it Up
The origin of the word Renaissance is from the Italian word Renascita meaning rebirth.
Is Web 3.0 the technological renaissance for eCommerce?
Just like in human history, it will be difficult to point out one fixed date when the web turned to the 3.0 version. Instead, it is an ongoing transition that necessitates the development of technology on multiple levels.
Even, as of now, all these technologies have found application on the web ― but not to the scale as envisioned in web 3.0.
If these are developed to point that they offer an ecosystem as mentioned in this article, and find a way around the challenges and complexities ― they have the potential to disrupt the Web experience, inclusive of eCommerce, and gradually replace Web2.0 with the new version.
Although, there is still time for that to happen…
But, by judging the current trends in the industry, it can be safe to assume that the technology is well on its path to providing a paradigm shift in experiences for consumers and opportunities for technology providers and businesses alike.
And until the time when Web 3.0 is extensively applicable, practically viable, and can be commercially implemented ― startups can identify existing opportunities or take inspiration from unique marketplaces and start with their eCommerce business in the current scenario with existing technologies.
Capture existing eCommerce opportunities with robust technologies of the current times that let you reach a wide audience, enhancing the scope and appeal of the eCommerce business. Power your online business with niche-specific turnkey eCommerce marketplace software or reach us to consult experts to bring your business idea to life
FAQ
Ans: It is the cumulative shift that multiple technologies promise to bring to the Web. As envisioned by Tim Berners Lee, the “semantic web” as he called it, is anticipated to be brought on by these technologies. It is expected that the web will be truly free, and the machines will be able to “understand” just like humans.
- Which are the Web 3.0 Technologies?
Ans: This can be understood as the main technologies that will aid in better capabilities to extract, compute, and experience data, Moreover, some technologies will further support the transformative shift.
- Higher number of sensors and IoT devices for more data
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) and ML (Machine Learning) for better computation of data.
- AR (Augmented Reality) and VR (Virtual Reality) to better experience the computed data.
- DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology) like Blockchain to better store data.
- Faster internet networks like 5G allow more data to be transferred per second, leading to better experiences.
Additionally, better infrastructure and the evolution of devices will further aid in the users benefitting more from the advantages offered by these technologies.
- Is Web 3.0 eCommerce going to be any different for buyers?
Ans: Yes, Web 3 eCommerce is going to change the dynamics of the industry.
- With more data extraction touch points, they will be able to interact with the system much more emphatically.
- Better computation means that the data will be analyzed with more “human-like” results.
- AR, VR will allow consumers to make purchase decisions with a better analysis of the product.
- Blockchain will help them to own their data and leverage it to their advantage and as per their preference.
To sum up, the buyers will find eCommerce interactions more engaging, personalized, and even more automated.
- Will Web 3.0 eCommerce give more opportunities to businesses?
Ans: Yes, with Web 3.0 eCommerce, existing major players will get more tools to engage buyers – attract them to buy more with interactive shopping experiences, leverage big-ticket products, and more – adding newer transactions to their existing system.
Smaller businesses, on the other hand, would be able to compete with the larger players with access to user data to offer more personalized shopping experience to the buyers, just like major players do. Furthermore, data will also help them to shape their business around buyer needs more effectively.
Moreover, Web 3.0 eCommerce is also going to augment operations and supply chain activities, benefitting all involved in the entire eCommerce ecosystem.






